Advanced Report Tabs¶
The Advanced report presents all variants identified in the index case that meet the analysis filters previously set in Advanced report settings. In every view of the Advanced report, only variants present in the index case are displayed. Findings are organized by category and displayed in a series of tabs, including the following:
Note
The tabs displayed depend on the study type that was selected when the study was created (see also Creating a new study).
Candidate Genes¶
The Candidate Genes tab lists variants from the index case that are found in the candidate genes previously selected for the study (based on the signs, symptoms, and phenotypes of the study participants) in Study Overview and Advanced report settings. The report shows the variants in genes associated with the phenotypes of the index case that pass the criteria defined in the Advanced report settings, for example, AF, VEP impact, Call quality, and Read depth.
Results can be filtered by selecting the following subtabs:
All by Genes
All by Variants
Mode of inheritance subtabs

Candidate Genes tab on the Advanced report (Clinical workflow)¶
ACMG¶
The ACMG tab lists variants identified in the index case that are found among genes in the ACMG version 2 list of 59 genes, and that pass the criteria previously defined in Advanced report settings.
ACMG tab on the Advanced report¶
OMIM¶
The OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) tab lists variants identified in the index case that are found in OMIM genes, and that pass the criteria previously defined in Advanced report settings.
Results can be filtered by selecting the following subtabs:

OMIM tab on the Advanced report¶
Known Variants¶
The Known Variants tab lists variants identified in the index case that are reported as “pathogenic” or “unknown” in the ClinVar, HGMD (Human Gene Mutation Database), or OMIM databases. By default, any variant (rare or common) reported in any one of the three databases is listed on this tab (i.e., Cat1-1D variants). The Known Variants tab also includes variants from the internal project knowledge-base.
Results can be filtered by selecting the following subtabs:
Rare Pathogenic Known Variants - Variants identified in the index case that are reported as “rare” (MAF< 0.03 by default) or “pathogenic” (as reported by ClinVar, HGMD, and/or OMIM), and that meet the criteria for Cat1, Cat1B, and Cat1C (for information about variant categorization, see Variant Categorization)
All Publicly Known Variants - Variants identified in the index case that are reported in the ClinVar, HGMD, and/or OMIM (Cat1 variants) public databases with an allele frequency (AF) less than the Cat4 AF threshold previously selected in Advanced report settings (or Report settings). These may include more common variants and/or variants annotated as VUS or benign.
Variants with comments - Variants in the index case that include comments and annotations previously added by users in a project. Annotations may have been added in the selected study or in a separate study.
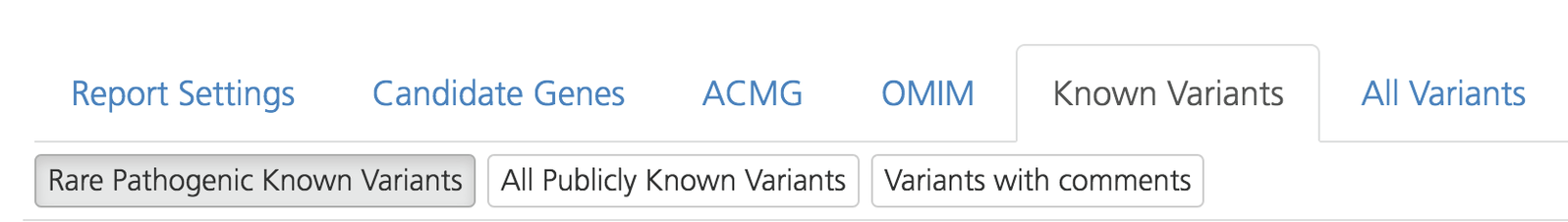
Known Variants tab on the Advanced report¶
All Variants¶
The All Variants tab lists all variants that meet the filtering criteria previously set in Advanced report settings, regardless of candidate genes for a particular phenotype.
Results can be filtered by selecting the following subtabs:

All Variants tab on the Advanced report¶
Advanced report subcategories¶
Results displayed on the Candidate Genes, OMIM, and All Variants tabs of the Clinical workflow Advanced report can be filtered according to the following subcategories, displayed in subtabs below each tab:
Variants in the Candidate Genes and All Variants tabs can be listed by genes or by variants, and filtered by mode of inheritance by selecting the inheritance pattern subtabs.
The following two types of variants are protected from further filtering:
Variants reported as “pathogenic” in ClinVar, OMIM, and/or HGMD (Cat1)
Variants with a “HIGH” VEP impact class
All by Genes¶
The All by Genes subtab list genes that are identified as having a variant. To view details about the variant identified for a particular gene, click Variants on the right-hand side of a selected row to open a Variant report. Clicking on the gene name in the list opens a drop-down menu to select a gene report.
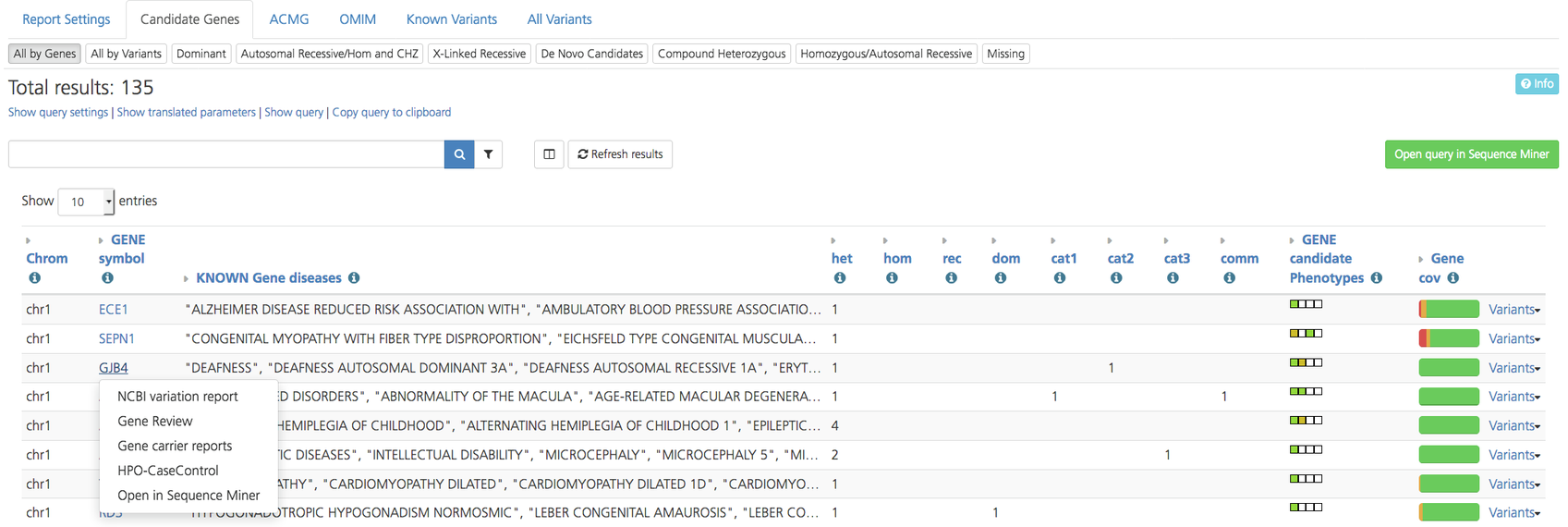
All by Genes subtab on the Advanced report¶
All by Variants¶
The All by Variants subtab lists variants by genomic position. By default, results are displayed in Table view. Attributes can also be customized for the analysis. Clicking on a variant in the list gives you the option to open the selected variant in Sequence Miner for real-time viewing and analysis of the aligned read, variant calling, and per base coverage files for the samples in the study. Clicking on the gene name opens a drop-down menu to select a gene report.
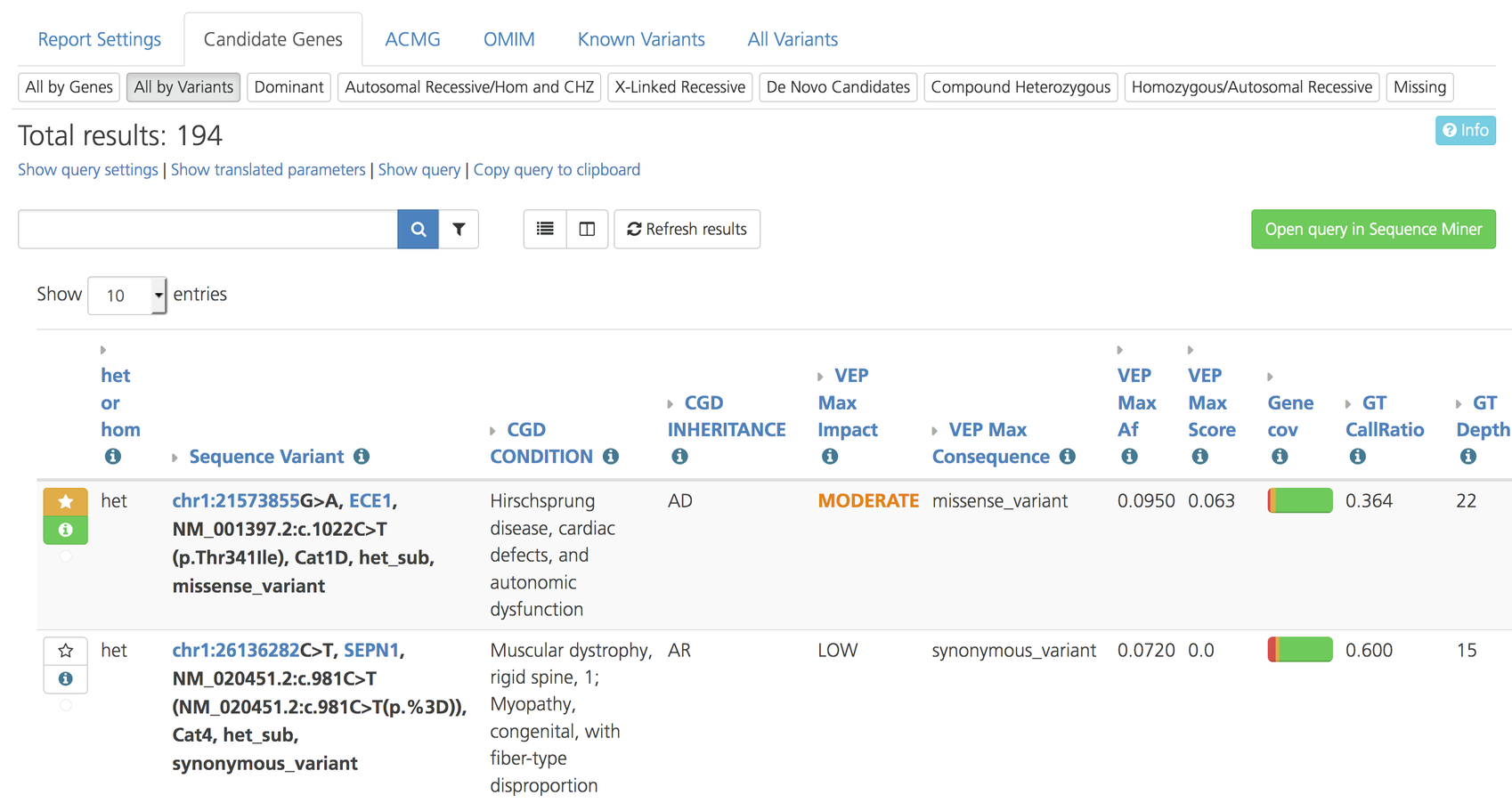
All by Variants subtab on the Advanced report¶
Mode of inheritance filters¶
The Candidate Genes and All Variants tabs can be filtered according to mode of inheritance or by de novo variants. These filters are allelic filters that compare the genotypes of the parents and siblings, if present, to the genotype of the proband (index case).
For example, in a trio or quad study the zygosity of the variants in each of the parents, proband, and sibling (if present) is determined. Next, the autosomal variants (i.e., chromosomes 1-22) identified in the proband are compared to autosomal variants called in each parent (and sibling) to determine whether the variant allele in the proband is inherited from the mother or father. After determining the source, the variant is defined as autosomal homozygous recessive, dominant, or compound heterozygous. For Dominant and Compound Heterozygous filters, at least one affected case is required to share the variant. If an index case has a variant not seen in either parent, the variant is labeled as De Novo and marked as an inheritance error on other subtabs. Lastly, a comparison of the variants is run in a similar fashion on the X chromosome only to determine X-linked inheritance, specifically by using the mother’s X chromosome to determine X-Linked Recessive variants.
The filters for calling heterozygous or homozygous variants (e.g., minimum % reads) can be adjusted in Advanced report settings.
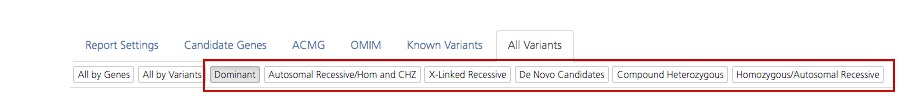
Mode of inheritance subtabs on the Candidate Genes and All Variants tabs of the Advanced report¶
Mode of inheritance subtabs are described in the table below:
Filtering option |
Description |
|---|---|
Dominant |
Filters autosomal variants present in either parent and proband; affected parent(s) must share variant, unaffected parent(s) must not have variant |
Autosomal Recessive/Hom and CHZ |
Filters autosomal variants that are homozygous recessive or compound heterozygous in the proband, and heterozygous in unaffected parents (or hom rec/chz in affected parent(s)). |
X-Linked Recessive |
Displays all the homozygous or hemizygous sequence variants appearing in males that follow an X-linked recessive inheritance model |
De Novo Candidates |
Two rounds of filters are applied:
|
Compound Heterozygous |
Genes harboring two or more filtered autosomal variants in the proband, where each variant is inherited from a parent; affected parent(s) must also be CHZ for the gene, unaffected parent(s) must not be homozygous for the variant |
Homozygous/Autosomal Recessive |
Filters autosomal variants that are homozygous in the proband and heterozygous in the parents of the proband (if unaffected) or homozygous in parent(s) (if affected) |
Missing variants¶
The Missing subtab is displayed on the Candidate genes tab only and lists potenitally pathogenic variants present in candidate genes that are absent or not sequenced in the index case due to an inheritance error or low coverage (e.g., homozygous in a parent but missing from the index case).
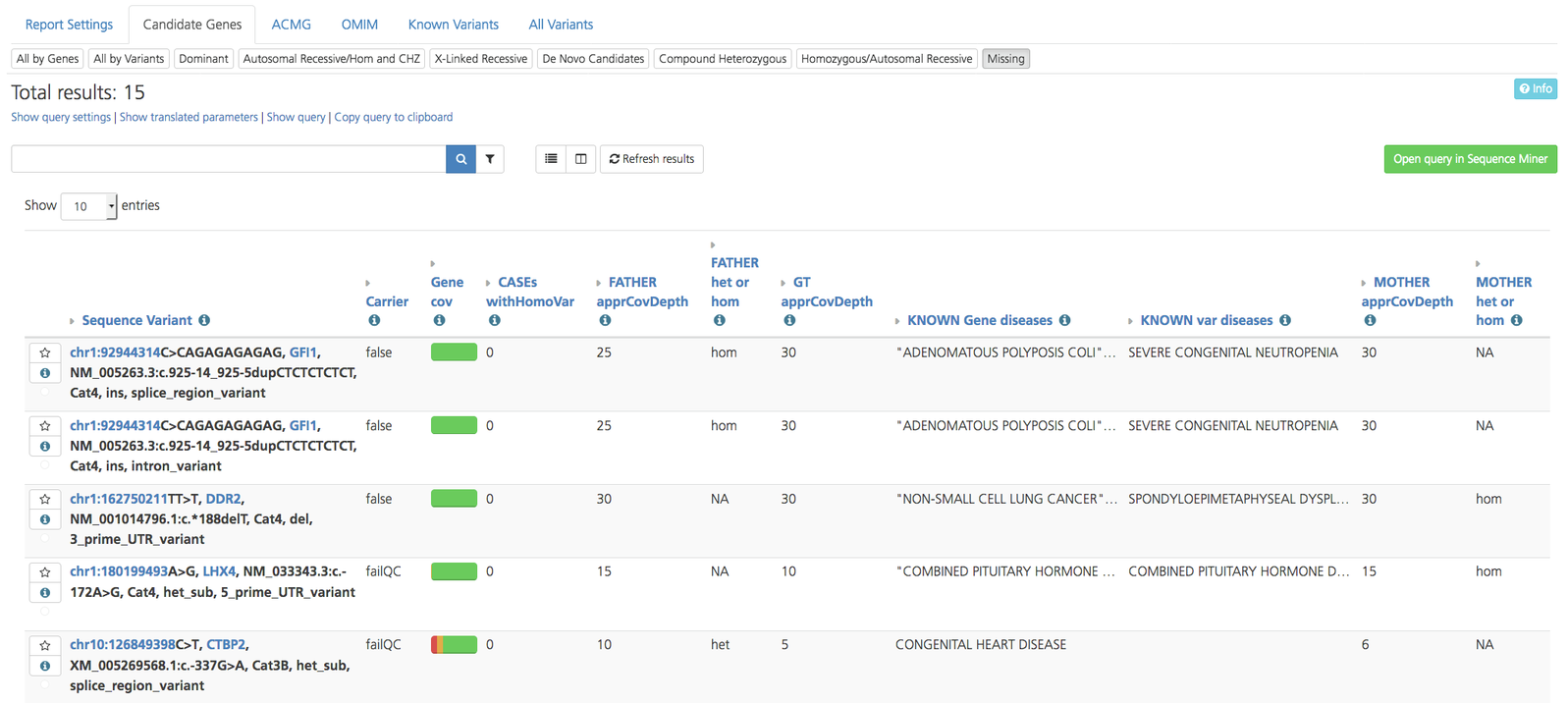
Missing variants subtab on Candidate Genes tab of Advanced report¶
Simplified workflow categories¶
Depending on the study type and workflow associated with a selected study, Advanced report findings may be displayed on the following tabs:
Variants
Genes
Missing (variants)
Reports
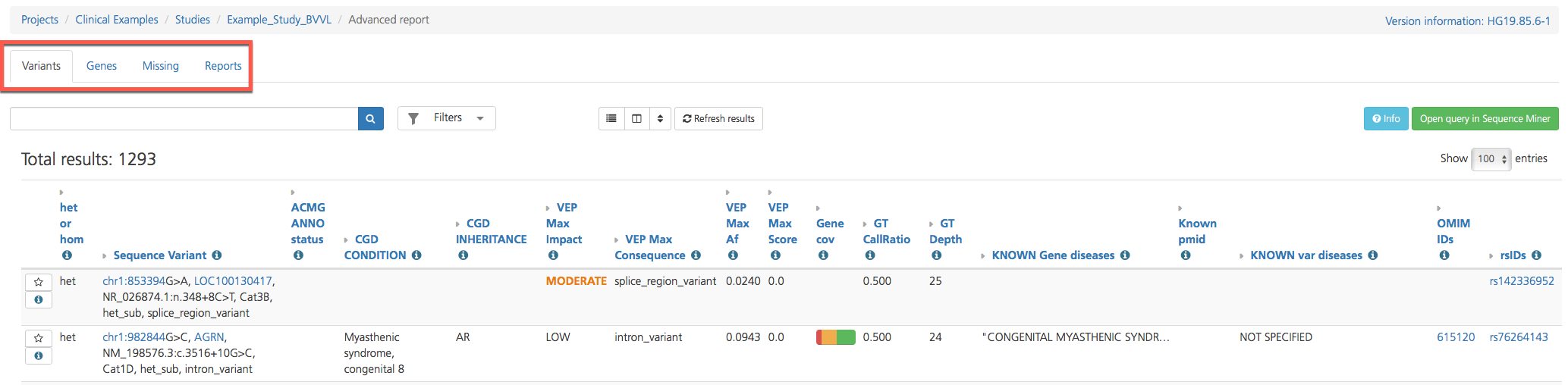
Advanced report categories in the Simplified workflow¶
For more information about Advanced report findings, see Understanding the Variant Listing.