Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) Settings¶
The Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) is a variant detection and classification algorithm. The VEP prediction is based on the following three factors:
The location of the variant in or near a gene
The predicted consequence of the variant on protein expression
The frequency of the variant in the human population
VEP uses two variant classification systems - SIFT (Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant) and PolyPhen2 (Polymorphism Phenotype) - to score the changes to the protein coding sequence, and generates a variant consequence prediction (VEP consequence). CSA summarizes VEP consequences into four categories of impact, based on the predicted consequence of the variant:
HIGH - Protein-truncating variants
MODERATE - Missense mutations, inflame indels, and splice-region variants outside the canonical splice site
LOW - Lower impact variants
LOWEST - Lowest impact variants
If a variant has more than one impact annotation in different transcripts, CSA reports the most severe or maximum impact notation. The full set of VEP consequences are available in Sequence Miner.
Note
Variants whose VEP consequence is classified as HIGH are protected from filtering in the Candidate genes and All variants tabs in the Advanced report view.
The figure below details the types of variants and the impact category to which they belong:
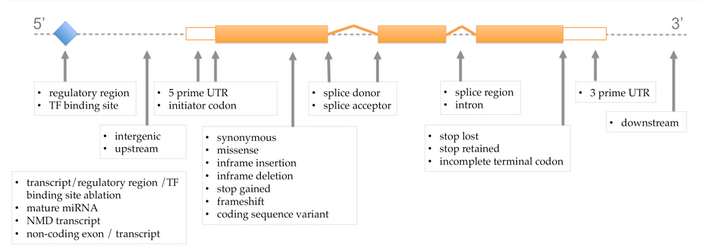
VEP variant consequences and their location in a transcript¶
VEP impact, VEP predicted consequence, and a translation of how to interpret the designated classes of variants are described in the following table:
Impact |
Consequence |
Description |
|---|---|---|
HIGH |
transcript_ablation |
A feature ablation where the deleted region includes a transcript feature |
HIGH |
splice_acceptor_variant |
A splice variant that changes the 2 base region at the 3’ end of an intron |
HIGH |
splice_donor_variant |
A splice variant that changes the 2 base region at the 5’ end of an intron |
HIGH |
stop_gained |
A sequence variant where at least one base in a codon is changed, resulting in a premature stop codon that leads to a shortened transcript |
HIGH |
frameshift_variant |
A sequence variant that causes a disruption in the translational reading frame because the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three |
HIGH |
stop_lost |
A sequence variant where at least one base in the terminator codon (stop) is changed, resulting in an elongated transcript |
HIGH |
start_lost |
A codon variant that changes at least one base in the initiator codon of a transcript |
HIGH |
transcript_amplification |
A feature amplification of a region containing a transcript |
MODERATE |
inframe_insertion |
An in-frame non-synonymous variant that inserts bases into a coding sequence |
MODERATE |
inframe_deletion |
An in-frame non-synonymous variant that deletes bases from a coding sequence |
MODERATE |
missense_variant |
A sequence variant that changes one or more bases, resulting in a different amino acid sequence and preserving the length of the transcribed protein |
MODERATE |
protein_altering_variant |
A sequence variant which is predicted to change the protein encoded in the coding sequence |
MODERATE |
splice_region_variant |
A sequence variant where a change has occurred within the region of the splice site within 1-3 bases of an exon or 3-8 bases of an intron |
MODERATE |
incomplete_terminal_codon_variant |
A sequence variant where at least one base in the final codon of an incompletely annotated transcript is changed |
LOW |
stop_retained_variant |
A sequence variant where at least one base in the terminator codon is changed but the terminator remains |
LOW |
synonymous_variant |
A sequence variant where there is no resulting change in the encoded amino acid |
LOW |
coding_sequence_variant |
A sequence variant that changes the coding sequence |
LOW |
mature_miRNA_variant |
A transcript variant located with the sequence of a mature miRNA |
LOW |
5_prime_UTR_variant |
A UTR variant in a 5’ UTR |
LOW |
3_prime_UTR_variant |
A UTR variant in a 3’ UTR |
LOW |
non_coding_transcript_exon_variant |
A sequence variant that changes a non-coding exon sequence |
LOW |
intron_variant |
A transcript variant occurring within an intron |
LOW |
NMD_transcript_variant |
A variant in a transcript that is the target of Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) |
LOWEST |
non_coding_transcript_variant |
A non-coding RNA transcript variant |
LOWEST |
upstream_gene_variant |
A sequence variant located in the 5’ upstream region of a gene |
LOWEST |
downstream_gene_variant |
A sequence variant located in the 3’ downstream region of a gene |
LOWEST |
TFBS_ablation |
A feature ablation where a deleted region includes a transcription factor binding site |
LOWEST |
TFBS_amplification |
A feature amplification in a region containing a transcription factor binding site |
LOWEST |
TF_binding_site_variant |
A sequence variant located in a transcription factor binding site |
LOWEST |
regulatory_region_ablation |
A feature ablation where a deleted region includes a regulatory region |
LOWEST |
regulatory_region_amplification |
A feature amplification of a region containing a regulatory region |
LOWEST |
feature_elongation |
A sequence variant that leads to the extension of a genomic feature with regards to the reference sequence |
LOWEST |
regulatory_region_variant |
A sequence variant located within a regulatory region |
LOWEST |
feature_truncation |
A sequence variant that leads to the reduction of a genomic feature with regards to the reference sequence |
LOWEST |
intergenic_variant |
A sequence variant located in the intergenic region between genes |
LOWEST |
intergenic_variant |
A sequence variant located in the intergenic region between genes |
LOWEST |
regulatory_region_fusion |
A feature fusion where the deletion brings together regulatory regions |
LOWEST |
regulatory_region_translocation |
A feature translocation where the region contains a regulatory region |
LOWEST |
TFBS_fusion |
A fusion where the deletion brings together transcription factor binding sites |
LOWEST |
TFBS_translocation |
A feature translocation where the region contains a transcription factor binding site |
References
Ensembl. Variant effect predictor. http://www.ensembl.org/info/docs/tools/vep/index.html
McLaren W, Pritchard B, Rios D, Chen Y, Flicek P, Cunningham F. Deriving the consequences of genomic variants with the Ensembl API and SNP Effect Predictor. Bioinformatics 26(16):2069-70(2010). (Full text)
Ensembl. Ensemble variation - predicted data. http://www.ensembl.org/info/genome/variation/predicted_data.html#consequences