FAQs¶
Following are some answers to frequently asked questions about using CSA and Sequence Miner.
How do I include variants in a report?
To add variants to a report, identify your variant of interest in the Variant listing and click the Info icon to open the Variant view window. In the Variant view, select a transcript for the variant you wish to add to the report. Add additional annotations as desired and click Update to add the variant to the report (see also Annotate Variants).
How do I add comments to variants, and will commented variants appear in the final report?
To add comments to a report, identify your variant of interest in the Variant listing and click the Info icon to open the Variant view window. In the Variant view, add annotations and comments as desired and click Update to add the variant to the report (see also Annotate Variants), along with the associated annotations or comments.
How do I know which version of an annotation was used in the analysis?
Clicking the Version link at the top right-hand side of the page in the Advanced report view opens the Version information window, which displays the source databases that constitute the NextCODE Reference Set and the version of each database.
I am writing the supplemental information for a paper. I want to find information on the exome target bases: what % were covered at 5X, 10X, 20X, and 30X, how many variants are in the coding regions, and how many were missense, frameshift, non-sense, misstop/mis/start, inframe insertion deletion, splice site, and synonymous?
There are several ways to pull out the coverage information you need, but the most straightforward way is to open the Data query window in Sequence Miner and issue the following command: gor source/cov/gene_cov_coding_seg.gord -f LIN_001_DABB10422 | where gene_symbol in ('PAH’)
If you are interested in the coverage of each exon, you can use the Exon coverage report builder in Sequence Miner to report sequence read coverage and additional attributes for each exon.
For more information about Sequence Miner queries and report builders, see the Sequence Miner User Manual.
When looking at BAM alignments in the Genome Browser in Sequence Miner, occasionally there are reads that have “H” as their base or that have no color (e.g., are presented with a white background instead of orange and blue). What do the “H” and white background mean?
The “H” stands for hard-clipped reads, and the white background denotes soft-clipped reads. Hard-clipped and soft-clipped reads are represented in the BAM files with the characters “H” or “S” in the CIGAR column. Both hard-clipped and soft-clipped reads are used to indicate that the clipped portion of the read does not map to the reference.
How does BWA determine whether to mark unaligned bases as hard-clipped or soft-clipped?
If the same read aligns to two or more locations, in the top hit, BWA uses soft-clip to represent unaligned bases; in the secondary and supplement alignments, BWA uses hard-clip to represent unaligned bases.
What does “GL_Call” mean and how does it compare to GQ value given by the GATK?
There are several terms in the VCF that are generated by GATK. By default in CSA, a GQ value filter is set to >30 to filter out low-quality reads. The GQ (genotype quality) represents the Phred-scaled confidence that the genotype assignment (GT) is correct, derived from the genotype PLs. The PLs have three numbers which represent the likelihood of three possible genotypes. The GQ value is the second-smallest PL, but is capped at 99. In CSA, to make it more readable, information is extracted from VCF files to generate several more columns. For example, the GL_Call column takes almost the same value as GQ in VCF, but is not capped at 99.
In Sequence Miner, how do I import data from my own computer to a project?
In the Sequence Miner File Explorer, locate the file on your computer. Right-click the file and select Copy, and then navigate to the user_data folder in the project. In the user_data folder, select the destination directory, and then right-click and select Paste (note that by design, user_data is the only directory with write permission).
In Sequence Miner, how do I export data from a project to my own computer?
There are a few options to export data:
Select the data within any table, then copy and paste the data directly into an external application (e.g., Excel).
Save the file directly to your local computer by clicking the Save icon.
Save the file in your project’s user_data directory, then copy the entire file to your local computer.
How do I exclude specific variants or regions from my analysis in CSA?
It is possible to exclude either specific variants or entire regions from analysis in CSA. Any variants identified in an exclusion file are ignored, and are returned in an analysis. Note that exclusion files should be used with caution.
- Excluding variants:
Create a variant exclusion file. This file should be tab-separated and include the columns CHROM, POS, REF, and CALL, for example:
#Chrom Pos Ref Call
chr8 145584264 T C
Note: The Chrom column must contain string values like “chr8”, not simple integer values like “8”.
In Sequence Miner, save the file in the user_data folder, in the variant_files subdirectory.
Add the variant exclusion list in CSA. The file should be listed in Advanced Report > Report Settings > Custom reference sources > Exclusion variant file. After adding the file, click Update at the bottom of the page.
Confirm that the expected variants are excluded from the analysis.
Excluding regions: To exclude regions, the same procedure is used as for excluding variants, except for a few minor modifications.
Create a variant exclusion file. This file should be tab-separated and include the columns CHROM, REGION_START, and REGION_END, for example:
#Chrom Region_start Region_end
chr8 145584260 145584270
In Sequence Miner, save the file in the user_data folder, in the region_files subdirectory.
Add the variant exclusion list in CSA. The file should be listed in Advanced Report > Report Settings > Custom reference sources > Region file. After adding the file, click Update at the bottom of the page.
Confirm that the expected variants are excluded from the analysis.
How do I restrict the maximum allele frequency to a specific set of allele frequencies?
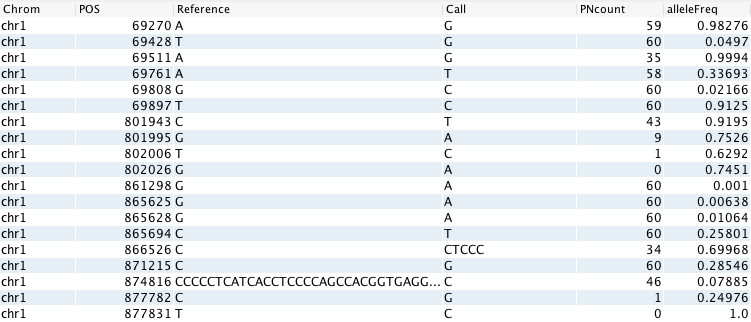
To perform Mendelian analysis, you can select own file with allele frequencies. The file must be in the GOR format with additional columns for alleleFreq and PNcount (the Varstat dialog can be used to calculate such allele frequencies), with these exact column names (see example below). Save the file in the user_data folder, in the var_statistics subdirectory in order to select it in the Custom reference sources subtab on the Advanced report settings tab of the Study Overview (or the Report settings tab of the Advanced report).
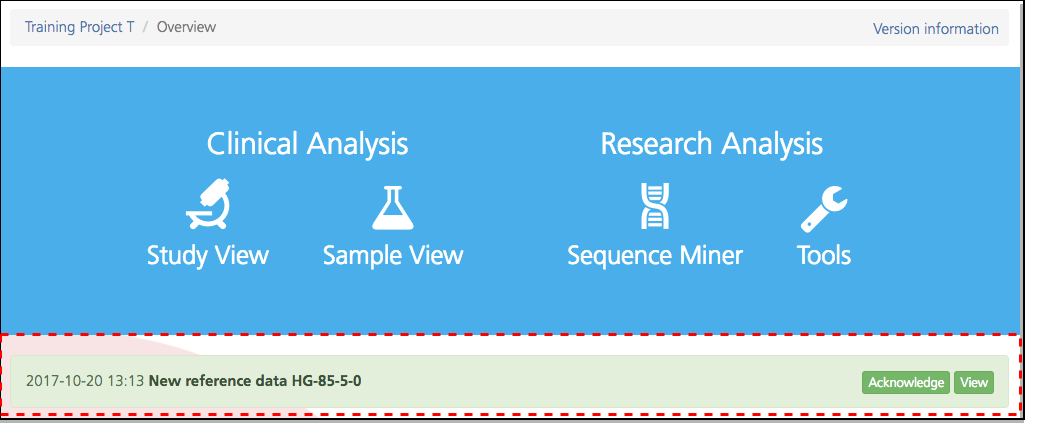
How often are the reference databases updated, and where can I find version information about the reference data?
The reference databases are updated quarterly. When a new reference data package becomes available, an announcement appears at the bottom of the CSA dashboard. By default, all new studies will use the new reference data, while existing studies will remain unchanged. Clicking the Version link at the top of any page in CSA opens the Version information window, where you can view current version information (see also Studies).
To see reference version information in Sequence Miner, locate the ref directory in the File Explorer and open the version.txt file.
Where do I upload a pedigree manifest file to create a study?
A pedigree file can be loaded in either of the following two ways:
In the Sequence Miner File Explorer, locate the file from your local drive in the computer folder and copy it to the user_data folder.
Provide the pedigree manifest as part of the payload with the BAM/VCF. It will automatically be reflected in the Participants.rep file in the SubjectReports folder in Sequence Miner.
Why is the annotation for my indel of interest in a slightly different position in external databases?
This discrepancy may result from differing methods for indel alignment. CSA left-aligns all genomic locations and right-aligns cDNA positions. External clinical databases such as ClinVar, HGMD, and OMIM are right-aligned, while external frequency databases such as ExAC are left-aligned. This difference can result in indels annotated in external databases having a slightly different associated position than in CSA.
Where can I view or modify phenotype information for my subjects in Clinical Sequence Analyzer(CSA) and Sequence Miner?
Phenotypes can be registered to an individual or to a study and there are several places from which to view or modify phenotypes:
In CSA, phenotypes registered to individuals can be reviewed and modified from the Samples page or from the Participant setup tab of the Study Overview.
A summary of phenotypes registered to all subjects in the selected study is available on the Phenotype summary tab of the Study Overview.
A summary of all phenotypes registered to the selected study is available on the Information tab of the Study Overview.
In Sequence Miner, a summary of phenotypes registered to all subjects in the project is available in the
SubjectReports/Phenotypes.repfile.